Solid-State vs Lithium-ion Batteries: Evolution and Principles of Operation

Evolution of Batteries
Batteries are at the heart of modern technological development, powering everything from portable devices to electric vehicles (EVs). Two key technologies dominating the era are Lithium-ion and Solid-State batteries.
Lithium-ion Batteries:
First introduced in 1991 by Sony, Lithium-ion batteries marked a significant milestone in battery technology. With high energy density, lightweight design, and reduced production costs when manufactured in large volumes, these batteries have become ubiquitous in portable devices, electric vehicles, and various household appliances.
Solid-State Batteries:
Building on Lithium-ion technology, Solid-State batteries replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid one, enhancing safety, longevity, and efficiency. While still in the testing and development phase, Solid-State batteries are seen as the future of battery technology.
Working Principles of Batteries
1. Lithium-ion Batteries
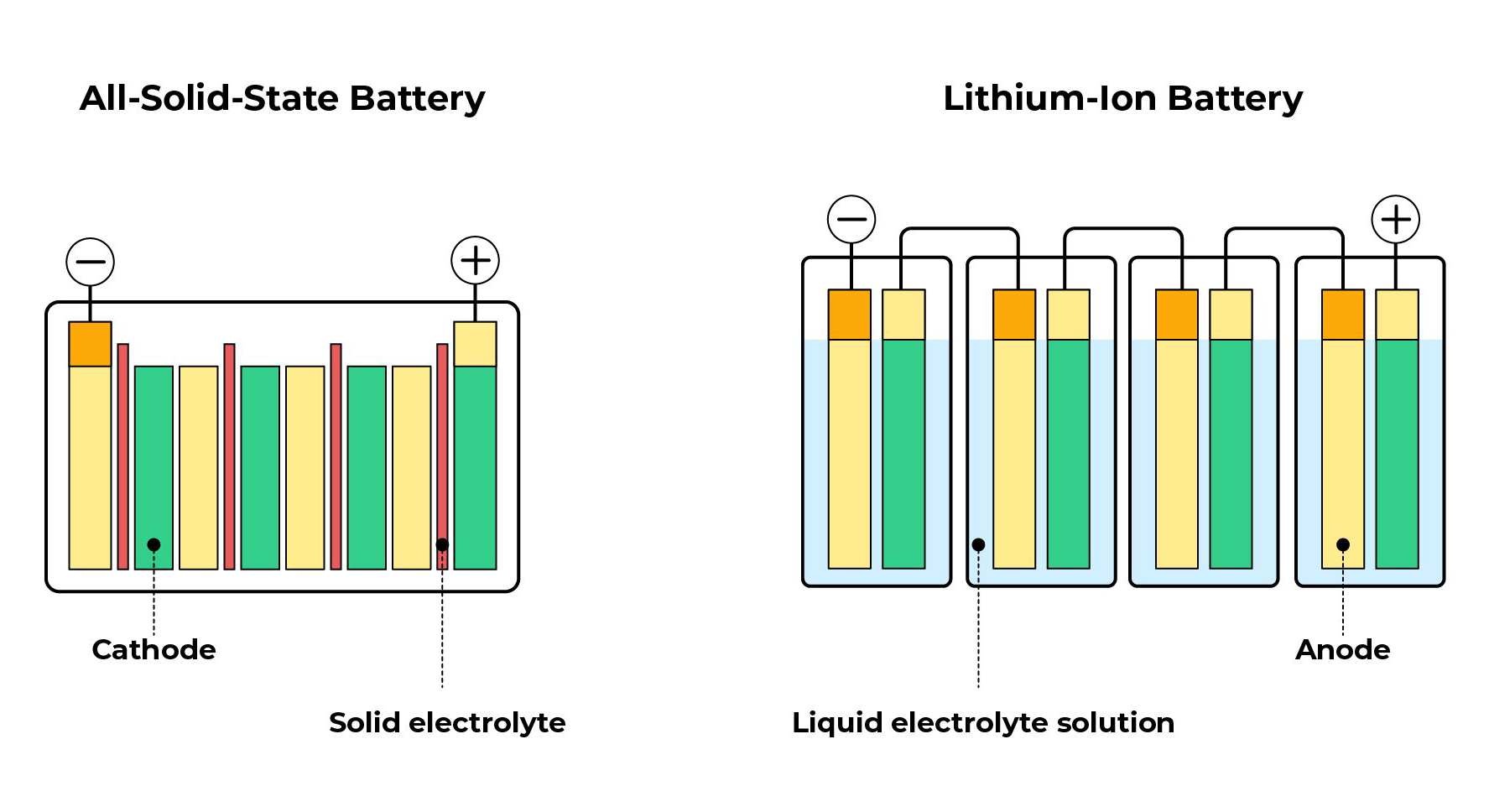
Structure:
- Cathode: Lithium oxide
- Anode: Graphite
- Electrolyte: Liquid that facilitates the movement of lithium ions
- Separator: Separates the cathode and anode to prevent short circuits
Operation:
- Charging: Lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode.
- Discharging: Lithium ions move back from the anode to the cathode, releasing electrical energy.
2. Solid-State Batteries
Structure:
- Cathode: Lithium oxide
- Anode: Lithium metal or silicon
- Electrolyte: Solid material, typically ceramic or polymer-based
Operation: Lithium ions move through the solid electrolyte between the cathode and anode, similar to Lithium-ion batteries. However, the absence of flammable liquids makes them significantly safer.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Aspect | Lithium-ion Batteries | Solid-State Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | - Lower production cost | - Safer (no flammable substances) |
| - Widely adopted, ready for immediate use | - Higher energy capacity | |
| - Lightweight with high energy density | - Longer lifespan | |
| - Resistant to extreme temperatures | ||
| Disadvantages | - Risk of short circuits and fire | - High production cost |
| - Shorter lifespan with frequent charging | - Limited commercial production | |
| - Unsuitable for extreme temperatures | - Still under development |
Progress in Solid-State Battery Development
- Toyota: Plans to launch EVs with Solid-State batteries by 2027, focusing on increased driving range and reduced charging time.
- Volkswagen: Partnering with QuantumScape to develop Solid-State batteries, with commercial production expected soon.
- Nissan: Aiming to introduce Solid-State batteries in EVs by 2028, targeting cost reduction and performance enhancement.
Summary
As of 2024, most EVs still rely on Lithium-ion batteries due to their stability and reliability. Solid-State batteries, though still in the development and testing stages, are expected to feature in next-generation EVs in the coming years.
Note:
Choosing the right battery technology should depend on usage requirements and budget to achieve optimal results. Adding further details about emerging technologies and real-world applications can make your blog even more engaging!